Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there are two main types, Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, they both share one major similarity: the body’s inability to regulate blood sugar properly. For individuals who have untreated diabetes, this issue becomes a serious concern that can lead to a wide range of health problems, some of which can be life-threatening. The impact of untreated diabetes is profound, and those who don’t manage the condition properly are likely to experience complications that affect various organs and systems in the body.
In this article, we’ll explore what happens when diabetes is left untreated, the symptoms and long-term effects of untreated diabetes, and how individuals can manage and prevent these complications by seeking proper care. We’ll also discuss how lifestyle changes and medication can significantly improve quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
What Happens When Diabetes Is Left Untreated?
For individuals who have untreated diabetes, blood sugar levels remain high for extended periods of time. Normally, the body uses insulin to help glucose (sugar) enter cells, where it can be used for energy. However, in individuals with diabetes, either the body doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1) or the insulin is not used effectively (Type 2). When diabetes is untreated, the glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar.
Read too: What is Diabetic Profile Test? A Complete Guide to Understanding Its Importance and Procedure
If left untreated for long periods, this condition can cause significant harm to various organs and systems in the body. The longer high blood sugar remains uncontrolled, the higher the risk of complications.
Common Symptoms of Untreated Diabetes
When diabetes is untreated, the body reacts in several ways, leading to noticeable symptoms. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination: High blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter the glucose, leading to excessive urination. This, in turn, leads to dehydration, causing the individual to feel very thirsty.
- Fatigue: Without proper insulin function, glucose cannot enter the cells to provide energy, leaving the person feeling tired and sluggish.
- Blurry vision: High blood sugar can affect the lenses of the eyes, leading to blurry vision.
- Unexplained weight loss: In Type 1 diabetes, the body may begin to break down muscle and fat for energy, resulting in weight loss.
- Slow healing of wounds: High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal, making even minor cuts or injuries take longer to recover.
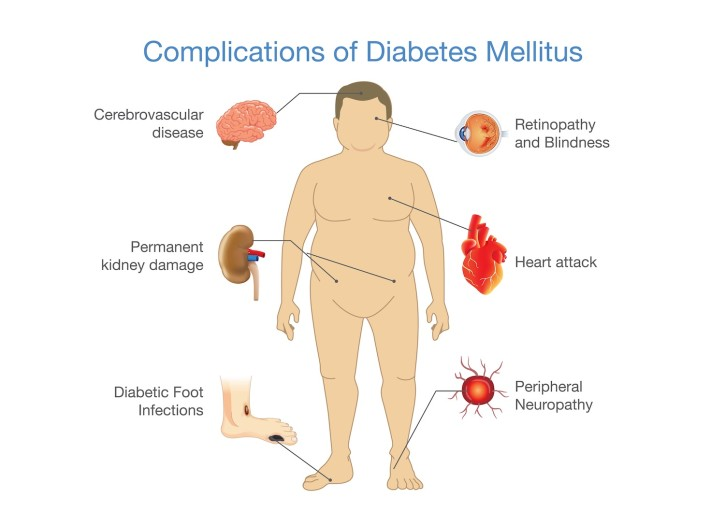
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Untreated Diabetes?
For individuals who have untreated diabetes, the risks increase as high blood sugar levels persist. Over time, untreated diabetes can lead to a variety of long-term complications that affect multiple organs in the body. These complications can cause significant health problems and may even result in disability or death if not properly managed. Some of the most common long-term effects include:
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Untreated diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease (PAD). High blood sugar damages blood vessels and nerves, leading to reduced blood flow. Over time, this can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
2. Kidney Damage (Diabetic Nephropathy)
The kidneys play an essential role in filtering waste from the blood. However, high blood sugar levels over time can damage the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney disease. This condition, known as diabetic nephropathy, can eventually result in kidney failure if not treated. Individuals with untreated diabetes are at a higher risk of needing dialysis or a kidney transplant.
3. Nerve Damage (Diabetic Neuropathy)
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that affects the peripheral nervous system. Untreated high blood sugar can damage the nerves throughout the body, especially in the hands, feet, and legs. This can cause numbness, tingling, pain, and even loss of sensation. In severe cases, diabetic neuropathy can lead to amputations, as the individual may not feel injuries or infections in their extremities.
4. Eye Problems (Diabetic Retinopathy)
Untreated diabetes can lead to diabetic retinopathy, a condition in which high blood sugar damages the blood vessels in the retina, the part of the eye that is responsible for vision. Over time, this damage can lead to blurry vision, cataracts, glaucoma, and even blindness if left untreated. Regular eye exams are crucial for individuals with diabetes to detect problems early on.
5. Increased Risk of Infection
High blood sugar weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Individuals with untreated diabetes are more prone to frequent infections, especially in the urinary tract, skin, and gums. Poor circulation due to damaged blood vessels also impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds, further increasing the risk of infection.
6. Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening condition that occurs most commonly in individuals with Type 1 diabetes, though it can also occur in those with Type 2 diabetes under certain circumstances. When the body cannot use glucose for energy due to a lack of insulin, it starts breaking down fat, producing ketones. A buildup of ketones in the blood can lead to acidosis, which causes nausea, vomiting, confusion, and in severe cases, coma or death. DKA requires immediate medical attention.
7. Skin Conditions
Diabetes can lead to various skin conditions such as bacterial and fungal infections, dry skin, and diabetic blisters. People with untreated diabetes may also experience slower skin healing, which can make even minor cuts and bruises more problematic.
Why Seek Treatment for Diabetes?
Individuals who have untreated diabetes are likely to experience many of these serious complications. However, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to prevent or manage these effects effectively. Seeking treatment for diabetes early on is critical in avoiding long-term damage. Here are a few reasons why it’s essential to manage diabetes:
1. Prevent Complications
By managing blood sugar levels with medication, diet, exercise, and regular monitoring, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
2. Improve Quality of Life
With proper diabetes management, individuals can lead a healthy and active life. Keeping blood sugar levels within a target range helps prevent symptoms such as fatigue, thirst, and blurry vision, which can greatly improve daily functioning.
3. Reduce Healthcare Costs
Early intervention and management of diabetes can reduce long-term healthcare costs. Preventing complications through treatment and lifestyle changes can help avoid costly medical procedures, hospitalizations, and medications.
4. Mental Well-being
Living with untreated diabetes can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress due to the constant uncertainty and worry about health. By getting treatment and managing the condition effectively, individuals can experience better mental and emotional well-being.
Managing Diabetes Effectively
Effective diabetes management involves several key components, which can be tailored to the individual’s needs. Some of the most important aspects of managing diabetes include:
- Medication: People with Type 1 diabetes need insulin to regulate blood sugar, while those with Type 2 diabetes may use oral medications or insulin, depending on their needs.
- Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet that controls carbohydrate intake is vital for managing blood sugar. Consulting a dietitian can help individuals create a meal plan that works for their specific condition.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, helping the body regulate blood sugar levels more effectively.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar: Regularly checking blood glucose levels is essential for understanding how diet, exercise, and medication affect blood sugar.
- Stress Management: Stress can raise blood sugar levels, so practicing relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, is essential for managing diabetes.
Conclusion
For individuals who have untreated diabetes, the risks of serious health complications are high. Chronic hyperglycemia can lead to heart disease, kidney damage, nerve problems, and more. However, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, these risks can be managed effectively. The key to preventing complications is early diagnosis, consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels, and adherence to a healthy lifestyle. If you or someone you know is living with untreated diabetes, it’s never too late to seek medical attention and make the necessary changes to live a healthier life.
Leave a Reply